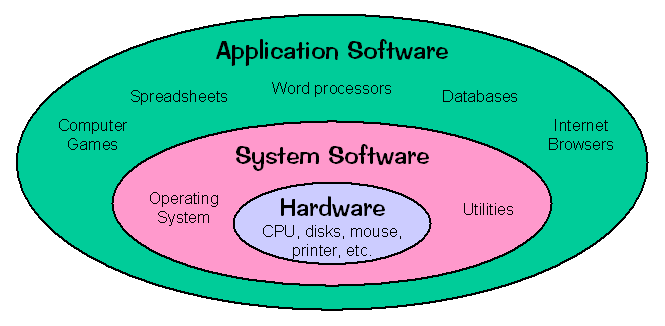
Operating system (OS) is an Integrated set of programs that control the resources of a computer system.OS provides its user with an interface or virtual machine that is more convenient to use then the bare machine.
Objectives of an OS are:
- Making a computer system convenient to use.
- Managing the resources of a computer.
- Provide an environment in which a user can execute a programs.
- Allow user to use the computer hardware in an efficient manner.
Types of operating System:
Below is a basic list of the types of operating systems and a few examples of operating systems that fall into each of the types.
1)Graphical User Interface- a GUI operating system contains graphics and icons and is commonly navigated by using a computer mouse. See the GUI definition for a complete definition. Examples of GUI operating systems are:
System 7.x
Windows 98
Windows CE2)Multi-user – A multi-user operating system allows for multiple users to use the same computer at the same time and different times. See the multi-user definition for a complete definition. Examples of operating systems that would fall into this category are:
Linux
Unix
Windows 20003)Multiprocessing – An operating system capable of supporting and utilizing more than one computer processor. Examples of operating systems that would fall into this category are:
Linux
Unix
Windows XP4)Multitasking – An operating system that is capable of allowing multiple software processes to run at the same time. Examples of operating systems that would fall into this category are:
Linux
Unix
Windows 85)Multithreading – Operating systems that allow different parts of a software program to run concurrently. Examples of operating systems that would fall into this category are:
Linux
Unix
Windows XP